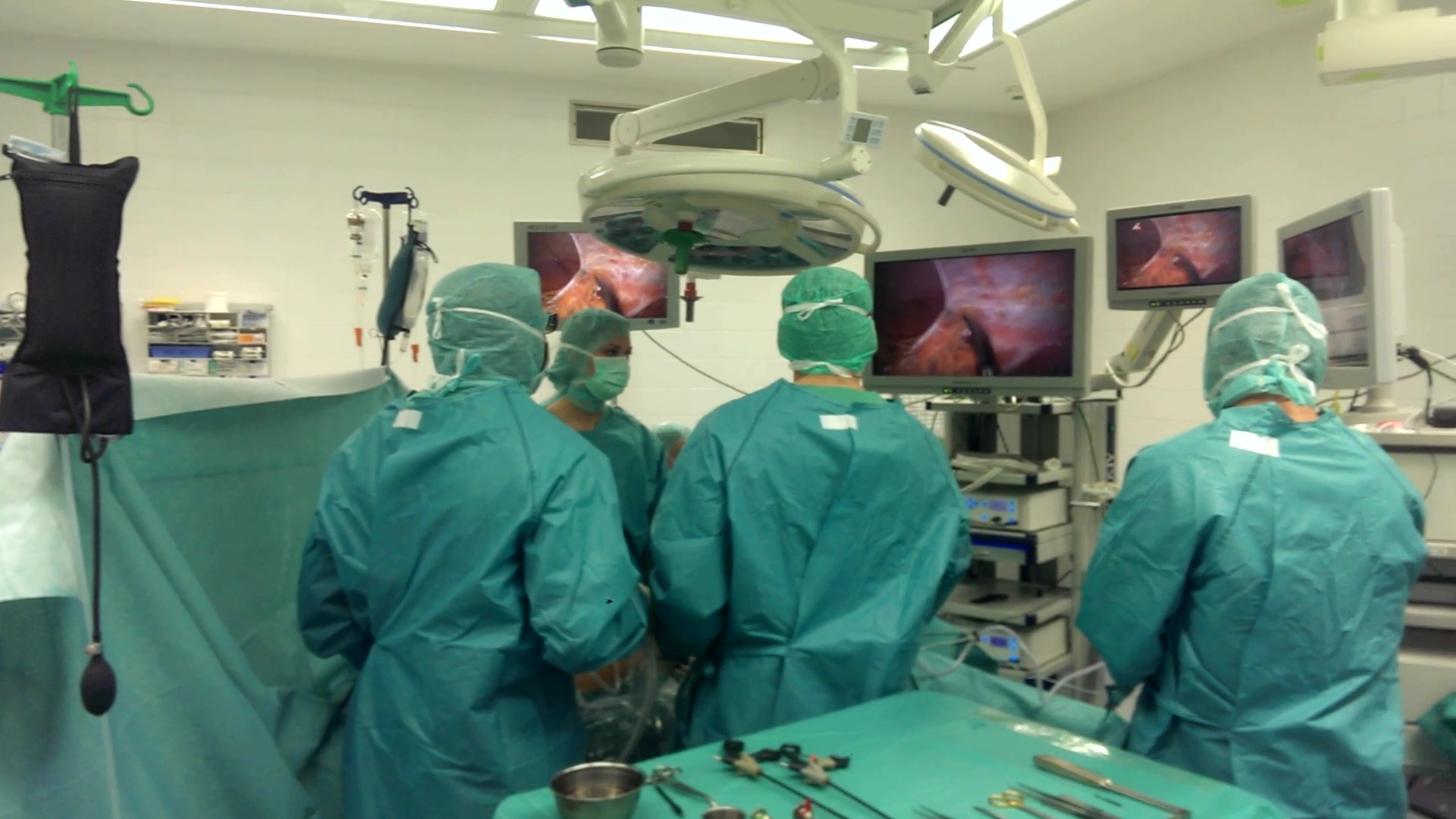
Laparoscopy is the biggest revolution in the field of Surgery during the last three decades. Laparoscopy is a technologically advanced surgical technique that allows to perform simple or complex procedures by using small skin incisions and specially designed instruments. Initially, laparoscopic surgery intended to minimize the extent of tissue injury and postoperative pain, but soon it emerged as an entirely new medical specialty (minimally invasive surgery), including the recent technology of robotic surgery.
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.